Mars Desert Research Station
Mission Summary
Crew 288 – Phobos
Dec 9th, 2023 – Dec 23rd, 2023
Crew Members:
Commander and Crew Astronomer: Dr. Cesare Guariniello
Executive Officer: Riley McGlasson
Crew Geologist: Hunter Vannier
Crew Engineer: Jesus Adrian Meza Galvan
Health and Safety Officer: Jilian Welshoff
Green Hab Officer: Ryan DeAngelis
Crew Journalist: Lipi Roy
Acknowledgements:
The entire Crew of MDRS 288 would like to express their gratitude to the many people who made this mission possible: our deepest thanks to Dr. Robert Zubrin, President of the Mars Society; Sergii Iakymov, MDRS Director, who assisted us in-situ and helped us troubleshooting the little problems we encountered; Dr. Shannon Rupert, who provided research advice and valuable support remotely; James Burk, Executive Director; Peter Detterline, Director of Observatories, who trained and assisted our Crew Astronomer before and during the mission; Michael Stoltz, The Mars Society Liaison, Media and Public Relations; Bernard Dubb, MDRS IT coordinator; Dr. Kshitij Mall and the Purdue Mission Support staff; the Purdue faculty who greatly helped us in the selection process of Crews 288 and 288 (Phobos and Deimos); all the departments and people at Purdue University and the external sponsors who supported this mission; and all the unnamed people who work behind the scene to make this effort possible, and who gave us a chance to be an active part of the effort towards human exploration of Mars.
Mission description and outcome:
MDRS 288 “Phobos”, twin of mission 289 “Deimos”, is the sixth all-Purdue crew at MDRS. The mission was characterized by very high research quality –despite one project having to be cancelled due to delay in approval by the IRB– and extremely good performance both from a professional and a personal perspective. The diverse crew, including three women and four men, representing four countries and various departments at Purdue, and comprised of undergraduate students, Master’s students, PhD candidates, and professional staff, accurately represented Purdue’s honored tradition in the field of space exploration.
Crew 288 performed various research tasks, with a strong geological focus evident in the many EVAs covering all areas of MDRS and in the amount and quality of samples and scientific data collected. Engineering experiment, astronomical observations, and other research projects concerned with Mars exploration and the operations of astronauts on planetary surfaces were also successfully conducted.
The crew is planning to continue working on the data collected during this mission, to support the twin mission “Deimos”, and to participate in various outreach events, in order to spread awareness about MDRS missions and to foster awareness and passion for space exploration.
Figure 1. MDRS 288 Crew posing in front of the habitat. Left to right: GreenHab Officer Ryan DeAngelis, Commander and Crew Astronomer Cesare Guariniello, Health and Safety Officer Jilian Welshoff, Crew Geologist Hunter Vannier, Executive Officer (and Crew Pirate) Riley McGlasson, Crew Journalist Lipi Roy, and Crew Engineer Jesus Meza Galvan
As commander, I am personally extremely proud of this crew, which was capable to keep the highest level of fidelity and realism, without losing sight of the importance of light moments. After passing a rigorous two-phase internal selection process at Purdue, the crew followed training and bonding activities with passion and commitment. At MDRS, the crew properly followed safety and research protocols, performed as a tight group, and found an appropriate mix of research activities and personal time. Every crew member has been attentive to other people’s needs, respectful of differences, conscious of own and others’ goals and shortcomings, flexible and willing to learn and improve. The pace kept throughout the mission was a solid mix of long, fruitful, and professionally conducted EVAs, work in the laboratory and in the RAM, and slower-tempo personal and communal time in the habitat.
Summary of Extra Vehicular Activities (EVA)
After being trained in the use of rovers and in the safety protocols for EVA, the crew had ten excursions during rotation 288, two of which being the traditional short EVAs to Marble Ritual. The remaining EVAs were long excursion, where the crew greatly maximized time usage, especially the time spent walking and performing field activities, which was in average 92% of the total EVA time. The EVAs reached areas in the Mancos Shale (Skyline Rim), Morrison Formation (mostly along Cow Dung Rd), Dakota Sandstone (Candor Chasma), and looked into the Somerville Formation (Somerville Overlook). The EVA served multiple research projects and were used to train crew members who were unexperienced in geologic field work.
Table 1. Summary of EVA, indicating Sol of execution, total duration and distance covered, time and distance spent walking and performing activities, and time percentage spent in activities outside driving.
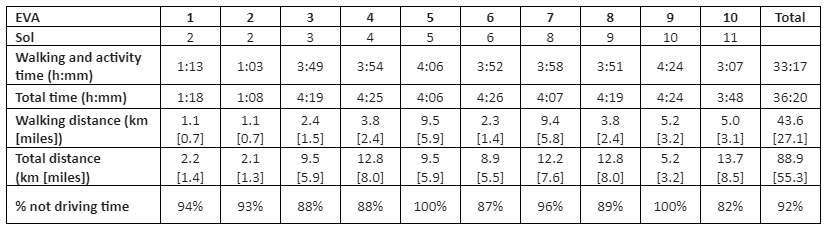
Figure 2. Satellite map of the EVAs performed by MDRS 288 crew and of the Station points where samples were collected
Summary of GreenHab Activities
Crew GreenHab Officer: Ryan DeAngelis
The GreenHab is in excellent condition. A lot of things have just been growing and maturing this rotation, with a few exceptions with various herbs and kale. A few of the cucumbers struggled a bit at the midpoint of the mission, exhibiting slowed growth and scarring on the stalks. This, however, was identified as growth marks perhaps exacerbated by slightly too much fertilizer. They are healthy and growing a lot as of the end of this mission. The tomato plants, planted by Crew 287, were caged and trimmed, and we even observed some small green tomatoes growing. In addition to harvesting fresh herbs daily for use in meals, we were able to create several small salads of arugula, kale, and lettuce. We planted more peas, mint, rosemary, carrots, and fennel for hopeful harvest and enjoyment by Crew 289. Overall, the GreenHab provided plenty of herbs and spices, as well as a fantastic place to de-stress for many crew members.
Science Summary
We had 9 separate projects that covered a range of topics. Some of them were EVA-related, while others were conducted at MDRS campus. One project was not conducted because IRB approval was not received in time. Overall, each project uniquely highlighted each crewmember’s strength and expertise, and expanded scientific, engineering, and human factor knowledge to support crewed exploration of Mars.
Research Projects:
Title: Noninvasive search for water
Author: Riley McGlasson
Description, activities, and results: GPR observations were taken at Watney Road, Compass Rock, Brahe Highway, and Hab Ridge. During EVA 3 two 3D GPR grids were taken at the turnoff to Watney Road (WR). One of these was a smaller 15’x15’ grid with 3’ spacing above the dry stream bed, which we used to train the rest of the EVA crew in how to conduct GPR surveys. The second WR grid (WR02) was 36’x36’ with 3’ spacing. WR02 encompassed the dry stream bed and adjacent sandy material. Six total 2D transects were also taken at three sample sites at Kissing Camel Ridge. Unfortunately, there was an error with the radar’s survey wheel, so none of these observations are usable. After EVA 3, this error was fixed, and more data was able to be collected during the remaining 3 GPR EVAs. During these, 100’ x 100’ 3D grids were taken with 10’ spacing at the survey sites, along with an additional 2D transect was taken across ~300’ of material in the same region for quicker analysis. We confirmed that the survey wheel error was fixed, and initial analysis of the 2D transect of the Compass Rock site produces reasonable velocity values for a damp sandy material. The 3D grids will be analyzed back on Earth and compared with spectroscopy data taken at the same sites.
Title: Refining orbital data with in-situ analysis
Author(s): Hunter Vannier
Description, activities, and results: Objectives of this study were to compare grain size predictions from orbital data to in situ observations, assess effectiveness of boulder sampling at the base of Kissing Camel Ridge in obtaining representative samples of upper units, and obtain and determine origin of volcanic rocks in the south.
Conducted EVAs to Barainca Butte, Kissing Camel Ridge and Hab Ridge to achieve these objectives. Boulder and grain size analyses were conducted during two EVAs to the Kissing Camel Ridge, which have been compared to orbital estimates. Some grain-size estimates were accurate, but subtleties in the orbital data were not appreciated until on foot, (ex. disproportionate darkening of orbital images from small cobbles). When sampling boulders at base at Kissing Camel and Hab Ridge, the top stratigraphic unit often dominated and other lithologies were not present (most converted to soil). Overall, sampling boulders was useful in obtaining samples from layers otherwise unreachable, but picking sites with less vs. more diversity of boulders was not accurately predicted.
We obtained spectra and samples of at least three igneous units (basaltic andesite, andesite, diorite) transported fluvially to the Barainca Butte area from both Henry Mountains and Capitol Reef. Near Barainca we identified a very high concentration of volcanic rocks in that area that were generally absent in regions north of Zubrin’s head. The fluvial pathway from source to MDRS is still not understood.
Spectra and samples have also been obtained within GPR grids to complement the radar data set with spectral and geologic characterization of the top ~5 cm of unique units within each grid. Preliminary spectral analysis of a site atop Hab Ridge within grey soil devoid of plants yielded a surface crust that appeared like significantly hydrated clay, yet the subsurface that yielded the majority of material appeared to have little hydration. There was also diversity in forms and depths of gypsum, some of which showed signs of oxidation. Not only does this compliment the science goals of radar, but is an important consideration when evaluating hydration of soils at depth for in-situ resource utilization.
Figure 4. (A): Obtaining spectrum of large rounded vesicular basaltic boulder. Red arrows points to abundant igneous rocks in the vicinity, Barainca Butte in the background. (B): Sampling station containing igneous rocks with multiple lithologies.
Title: Remote sensing for ISRU
Author(s): Cesare Guariniello
Description, activities, and results: The goal of this project is to test the use of remote sensing performed in various locations to support advanced In-Situ Resource Utilization. In particular, assessment of mineralogy via remote sensing will provide information about material abundance. Laboratory study of thermal inertia and its correlation with bulk size (sandy vs. rocky) will add one more variable to the study. Thermal Inertia is correlated to particle size and cohesiveness of the material, which in turn suggests the most appropriate tools to effectively collect the material for processing. Water content is assessed via the analysis of the depth of absorption bands in the spectra. This year’s focus has been on consolidated clay rocks. Samples have been collected for this project in the vicinity of Barainca Butte, at the foot of Skyline Rim, and along Galileo Road between Compass Rock and Somerville Overlook. These samples will be subject to experiments related to water content.
Title: Semiconductor processing
Author(s): Jesus Meza-Galvan
Description, activities, and results: The project was focused on the feasibility of basic semi-conductor manufacturing at the station. Two main experiments were conducted to explore silicon-oxide growth, and photolithography. The goal of the first experiment was to determine if oxide growth is possible in one of the lab ovens. A set of silicon samples were placed inside Oven #1 as shown in Figure 5a. A graduated flask with 1 liter of water was placed inside the oven just beneath the samples to maintain a high moisture environment. The samples were then annealed at a maximum oven temperature of 250 °C for a total of 2 hours, 4 hours, and 8 hours. Quantitative analysis of the oxide films will be performed using ellipsometry at Purdue. Qualitatively, there is no visual distinction between the samples indicating little to no oxide was formed. This is as expected given the temperature of the oven was lower than the typical growth temperature of silicon-dioxide in the range of 400 – 800 °C. In order to reliably grow oxide at the station, the oven temperatures must be increased. For the second experiment, a set of silicon samples with a photo-sensitive polymer (photoresist) was prepared prior to coming to MDRS. The laminar flow hood was outfitted to perform UV-exposure of photoresist as shown in Figure 5b. A Dremel stand was used as a makeshift photo-aligner to hold a handheld UV lamp at a constant distance away from the sample and perform controlled UV exposures of the resist as shown in figure 5c. A set of samples with varying exposure time, and varying working distance were made. Qualitatively, the experiment produced several good exposures of a microscope calibration pattern onto the photoresist layer. The success of the procedure will be determined quantitatively by measuring the dimensions of the samples produced against a calibrated microscope at Purdue.
Figure 5. Semiconductor Processing at MDRS. a) Silicon-oxide growth experiment in Oven #1. b) Photolithography set up inside laminar flow hood. c) Photolithography exposure.
Title: Reducing stress in isolated environment
Author(s): Lipi Roy, Ryan DeAngelis, Jilian Welshoff
Description, activities, and results: The crew consulted some of the sensors brought to MDRS for this project. However, formal research was not conducted, and test surveys were not administered, because IRB approval was not received in time for the mission.
Title: Astrophotography with the MDRS WF and Solar Observatory outreach
Author(s): Cesare Guariniello
Description, activities, and results:
Solar Observatory: visual observations on one day with the Crew Engineer and the Journalist. Various small problems with the telescope (modified Home Station, and some components left out of place by previous crews) were solved. The observatory bottom shutter also had to be troubleshot. All days not spent on EVA were at least partly cloudy during the day, thus preventing further solar observations.
Astrophotography: MDRS-WF was used to produce high-quality photos of M31 (Andromeda Galaxy), Barnard 33 (Horsehead Nebula), Leo Triplet, M42 (Orion Nebula), M1 (Crab Nebula) and some photos of smaller galaxy with quality that could be improved in postprocessing. Further WCS data are necessary to align images from the MLC-ROS16 telescope.
Title: Station monitoring
Author(s): Jesus Meza Galvan and Jilian Welshoff (proposed by Nathan Bitner – MDRS 289)
Description, activities, and results: The goal of this project is to study what information is most useful to analog astronauts during missions, as well as how this information is leveraged for day-to-day mission planning. A prototype of the sensor payload was completed which integrates temperature, humidity, VOC, CO2, and dust particle sensors with a raspberry-pi and battery package. The sensors have been coded by Purdue mission support who will remotely collect environmental data. Crew 289 will continue the project and create additional sensor payloads to place one monitoring station in each of the MSRS modules, as well as sensors on the air locks to determine if they are closed.
Title: Samples transportation with drones
Author(s): Cesare Guariniello
Description, activities, and results: In past missions at MDRS, drones have been used to prospect potential areas of geological interest. This conceptual project had the goal to prove the feasibility and usefulness of using a drone to transport payloads from the station to astronauts in EVA and vice versa. The capability of the drone to carry small payloads while maintaining maneuverability and safety was successfully tested before the mission. During the mission, part of the EVA to Skyline Rim (EVA #5) was spent in surveying the Hab Ridge for suitable locations for this experiment. Later, two crew members were trained in drone piloting, so as to be able to operate the small drone under the supervision of a crew member who holds a drone pilot license. During EVA #9, the drone was launched from the station with a small rock sample and a message onboard. Both items were received by the EVA astronauts, that successfully used the drone to return a rock sample to the station. The drone was then sent back with a food sample (representative of potential use of a drone to provide tools or support to astronauts on EVA), used by the EVA crew to record footage of the GPR experiment, before being flown back once more to the station.

Title: Chez Phobos
Author(s): Lipi Roy (et al.)
Objectives: Creating new recipes with shelf-stable food at MDRS
Description and Results: Crew 288 members proved that it was quite possible to create healthy, tasty recipes from shelf-stable food items at MDRS habitat. Many new recipes were successfully implemented and very much appreciated by the MDRS members. Riley’s Hab-burger, Ryan’s Pad-Thai and carrot cake, Cesare’s Italian pizza and baked ziti, Jilian’s Mujadara, Hunter’s spam fried rice and tuna-tomato pasta, Jesus’s Spanish rice, and my chickpea curry, kidney beans curry, and potato parathas; all created with minimal outside ingredients! For example, our ‘meal of the mission’ – spam fried rice was prepared using rice, dehydrated eggs, spam, dehydrated onions, dehydrated tomatoes, soy sauce, chilli peppers, salt, garlic powder, black pepper; all available in the hab!


You must be logged in to post a comment.