Crew 292 End-of-Mission Report

MANGALYATRI (Mars Explorers)
Mars Society Australia
February 4th – Feb 17th, 2024
Crew Members
Commander: Dr. Annalea Beattie
Crew Science Lead and Geologist: Bharti Sharma
Health and Safety Officer and Crew Biologist: Daniel Loy
Crew Engineer: Rajvi Patel
Green Hab Officer and Geospatial Information Specialist: Mehnaz Jabeen
Crew Astronomer and XO: Aditya Karigiri Krishna Madhusudhan
Crew Journalist and Geo-conservationist: Clare Fletcher
Mission Overview: Planning for Ladakh
Mangalyatri MDRS Crew 292 is a primarily Indian national crew fielded by Mars Society Australia. We have an overall focus on what we can learn here from the Mars Desert Research Station, Utah to build a Science Desert Research Station in the Himalayas, Ladakh, India. Ladakh is a very cold, high-altitude desert region, (3500 to 5700 metres above sea level) in northern India. It has lower levels of oxygen in its atmosphere and high levels of UV radiation. Its glacial deposits and regions, dune and intra dune ponds, hot springs, hypersaline lakes and permafrost regions are high-altitude environments for off-earth analogue and astrobiology research. Presently, there is no dedicated Mars analogue science research station in the southern hemisphere.
The members of Mangalyatri Crew 292 at the Mars Desert Research Station were chosen because of their research interests and their ability to think ahead to the future for a science desert research station in South Asia. Our crew shares a common goal yet each person has different objectives aligned to their research and field of knowledge, whether it be science, science operations, design, systems in the hab or green hab, art, astronomy or geoconservation. We are all driven by the science, carrying out field science and scientific research to compare different, extreme, terrestrial environments to understand more about the extraterrestrial. Our aim is also to develop frameworks for sustainable analogue research in terms of both science and science operations. See individual research reports for progress. All our field work has contributed to this project.
Exploring Planetary Analogue: Deciphering Geomorphometric and Slope Analysis across Analog Environments
Bharti Sharma in collaboration with, Dr. R. P. Singh (University of Allahabad), Dr. Jonathan A. Clark (Mars Society Australia) and Prof. Colin Pain (Mars Society Australia) and support of Crew 292.
The goal is to measure the slopes of outcrops, create a geomorphological map of the region, conduct geomorphometric analysis, and understand the processes that produced the region in comparison the slope angles and geomorphometry of Ladakh. This research provides insights into the geology and geomorphology of the region, which we can compare to the Martian landscape to detect parallels. So far, no extensive geomorphometric investigation of Hanksville has been conducted.
A total of 6 EVA has been conducted to get to the ground data from the field. First EVA was a training EVA, to get accustomed to the suit and Rover. Second and Third EVA was to get data from Cowboy Corner. Location points were collected from the site for different types of weathering, structural features such as cross bedding, rock type classification, general geomorphology to understand the chasm, meandering of river channels and ridges in the region. The fourth EVA on Kissing Camel Ridge’s western side estimated the slope from the bedding plane. Three measurements of the dip and strike have been obtained from the Kissing Camel Ridge. It was challenging to quantify dip and strike since the majority of the surface in the area has worn and eroded away from the parent rock. The locations of the fifth EVA were Compass Rock and Candor Chasma. The field data includes the kind of rock, the weathering patterns, and different landforms such as buttes, canyons, paleo-river channels, mesas, and caves. SRTM DEM has been used to create a basemap. The research area’s comprehensive geology and the literature review has been written. Geomorphometric analysis of Tso Kar, Ladakh, has already been completed. To comprehend the stratigraphy of the area, the Litholog has been developed from several sites. For post field analysis, the 32 fundamental morphometric variables will be used.

Survey benchmark, Hanksville, Utah, USA
Understanding frontier environments through drawing
Dr. Annalea Beattie, with full crew participation.
Through art making, this project focuses on boundaries, thresholds and environmental stewardship. This research project invites our crew to participate in an act of examination, to explore through drawing and painting beyond the boundaries and borders we create for ourselves as humans, in an unfamiliar, non-human landscape.
Crew 292 were provided with sketchbooks and drawing materials and a working studio table in the Science Dome to paint and draw something from their discipline or experience that might extend their understanding of simulation in this extreme desert environment. Or something that might help them explore the future. Almost all our crew have used drawing and/ or painting to reflect upon their position. Our astronomer Aditya has drawn the magnitude of celestial light he can see in our dark sky. Green Hab Officer Mehnaz has begun to draw the future – breathing life into barren planets through drawing a vision of the Green Hab for spacefarers living off-Earth. Observation in the field is a primary means of obtaining scientific knowledge for planetary field science and Crew Geologist Bharti Sharma and I drew geology together in the field on EVA #10 at Kissing Camel Ridge. We will work on the lithologic log for her comparative study of different kinds of deserts. The deliberate practice of geological field sketching in simulation is a sustainable method of gathering of data during field work. Crew Journalist Clare Fletcher drew rock samples removed from the desert. Clare is a geoconservationist and her project focuses on the practicalities of efficient and sustainable sampling. Drawing samples is a useful way of thinking through materials to inference and hypothesis. These samples have been returned to the site on our last day here at MDRS. I also have spent time drawing rock samples in the Science Dome, drawing basalt, concretions, gypsum, and the sandstone weathering. As I draw, I engage with this desert as a geological analogue for Mars. This research project is improvised, long-form and ongoing. Its results are not easily quantified nor is it data driven yet there is no doubt that art making in this confined context has potential to shift our perceptions and the capacity to affect change.

Drawing concretions in the Science Dome, 12-02-24
Investigating the Thermo-hydrological Dynamics of Green Hab: A Comprehensive Study on the Impacts of Temperature and Humidity on Evapotranspiration
Mehnaz Jabeen, in collaboration with crew member, Aditya Karigiri Krishna Madhusudhan
Overview:
Manipulated atmospheric variables in a controlled environment compared to natural environments can be shown to be pivotal to study and access the impacts of changes and estimation of PET, maximizing plant growth and resource efficiency. This research aims to delve into the thermo-hydrological dynamics within the controlled ecosystem of Green Hab, specifically focusing on nuanced interplay between temperatures, humidity, evapotranspiration (ET).
Objectives:
Explore spatial and temporal variations of temperature, humidity, and soil moisture within the Hab and different climatic environment within MDRS (artificial ecosystem).
Rigorously assess the effects of manipulated temperature and humidity conditions on evapotranspiration dynamics.
Employ climatic datasets from nearest climate centers.
Calculate Actual Evapotranspiration (AET) and Potential Evapotranspiration (PET) through established equations.
Apply the Budyko curve to decipher the ecosystem’s response to altered temperature and humidity regimes.
Current Status:
Obtained datasets the LOA Climate Center, Utah.
Data cleaning and processing.
Performing Pan Evaporation experiment to estimate evapotranspiration rates at different temperatures.
Performing experiments with newly sown seeds in similar pots with equal weights to study effects of varying temperature on plant growth.
Developing machine learning model to predict evapotranspiration using the datasets collected.
The technical rigor embedded in this research will not only contribute to our fundamental understanding of controlled ecosystem dynamics but will provide precise insights into optimizing temperature and humidity parameters for enhanced plant growth and resource management in artificial habitats especially in Ladakh (India) with extreme climate conditions and Mars-like terrain.
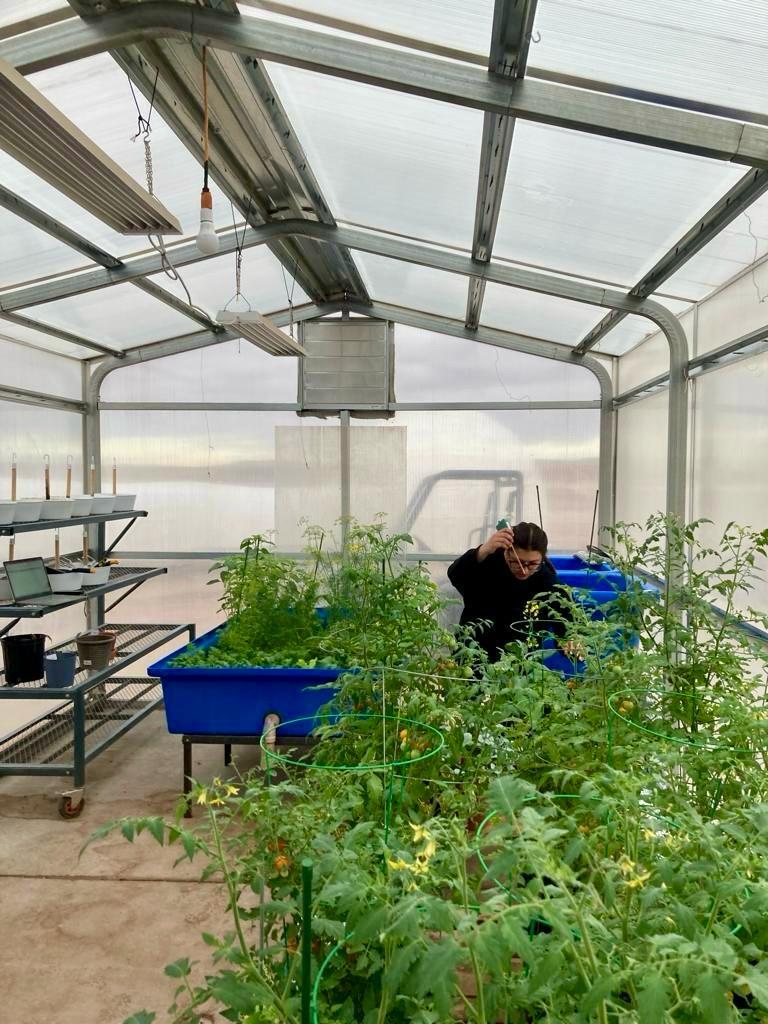
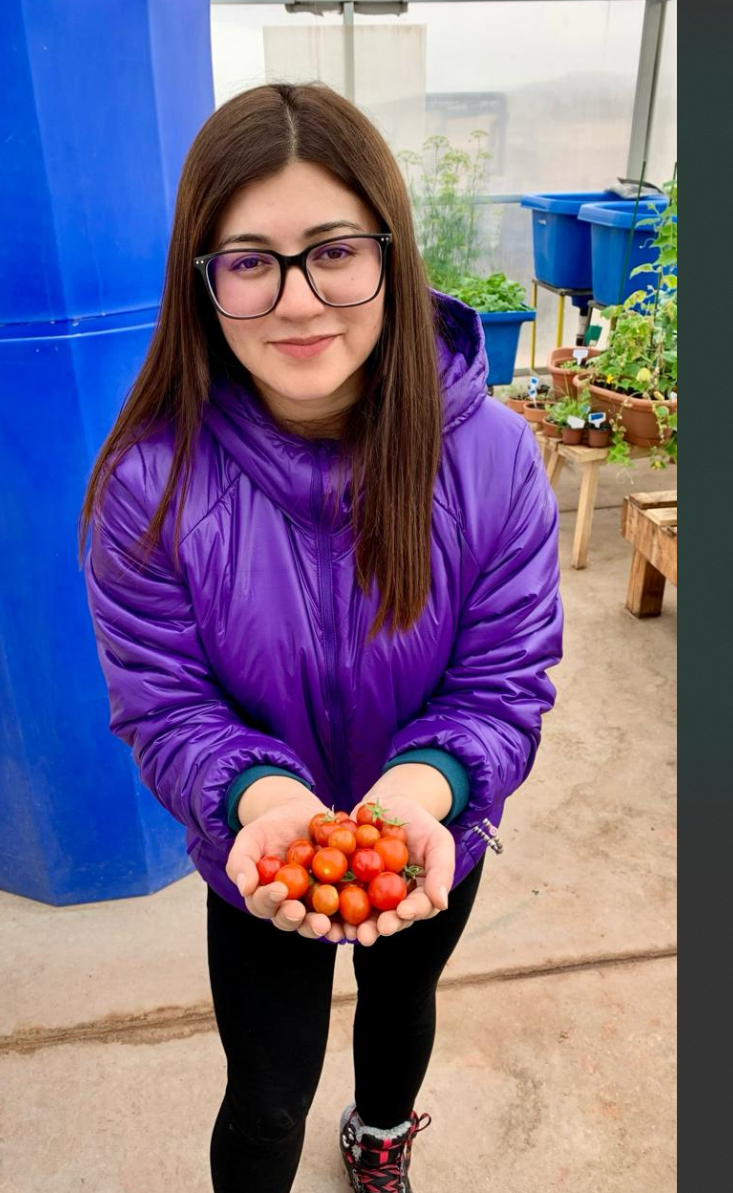


Green Hab Officer, Mehanz Jabeen in the Green Hab measuring the temperature of the crops and with the cherry tomato harvest.
Developing a method of simultaneous Mars exploration and exogeoconservation in the Mars Desert Research Station
Clare Fletcher, Crew 291 (Scientist) & 292 (Journalist), with thanks to all Crews 291 & 292.
Over the course of Crew 292 (and following on from Crew 291), Clare researched practical methods of geoconservation that don’t limit exploration and science, to apply these to both a possible future analogue station in Ladakh, and to Mars. Clare conducted 7 EVAs during 292 (and 8 during 291) to meet these goals, as well as analysis of field samples, and mapping of important geology and geomorphology. The key finding of Clare’s research was that geoconservation can’t be conducted effectively using remote operations work. Other notable findings include: the necessity of accessible baseline study sites and the lack of predictability of finding key study targets therefore necessitating exploration, science, and geoconservation to occur concurrently. When thinking about a research station in Ladakh, good baseline study needs should be identified early, and a code of conduct for fieldwork and sampling practices should be created that crews sign, acknowledging that they will adhere to it. Clare’s study highlights the importance of concurrent geoconservation, exploration, and science on Mars, and the necessity for detailed, crewed geological, geomorphological, and exogeoconservation studies due to limitations of remote operations. Detailed records should also be kept as each successive mission or crew will treat the landscape differently, meaning that both the landscape and knowledge of the area change concurrently and proportionally.
Use of portable laboratory equipment in a Martian analogue research station
Daniel Loy, Crew Biologist, with support from all Crew 292.
The aim of this project was to conduct research on the use of portable equipment in a Martian analogue simulation and environment: carrying out DNA extractions, PCR and gel visualizations with the Bento Lab portable PCR workstation.
Soil and water samples were collected by multiple crew members across different EVA’s for culture-dependant and independent DNA extraction using the Qiagen DNEasy Powersoil Pro kit. From 5 soil, 3 culture media, 2 water, 1 lichen, and 1 organic-looking deposit, two positive results were found from two of the soil samples. Using targeted PCR, Archaea and Fungi were identified to be within the soil in both S and S2 samples. The S soil sample also contained Bacteria, while this could not be identified within the S2 sample due to an amplication failure. The presence of functional genes was also investigated with the large subunit gene hhyL of the group 1h [NiFe]-hydrogenases found within both soil samples, and the sulfide:quinone oxidoreductase gene fragment sqr found within the S soil sample.
Successful extraction, amplification and visualisation of DNA and specific genes with this equipment shows that portable laboratory equipment can be used in extraterrestrial analogues to investigate the presence and functions of microorganisms. Pre-existing protocols for all processes were followed, meaning anyone, including non-biologists and having the correct equipment, would be able to replicate these methods including at the proposed Ladakh analogue research station.
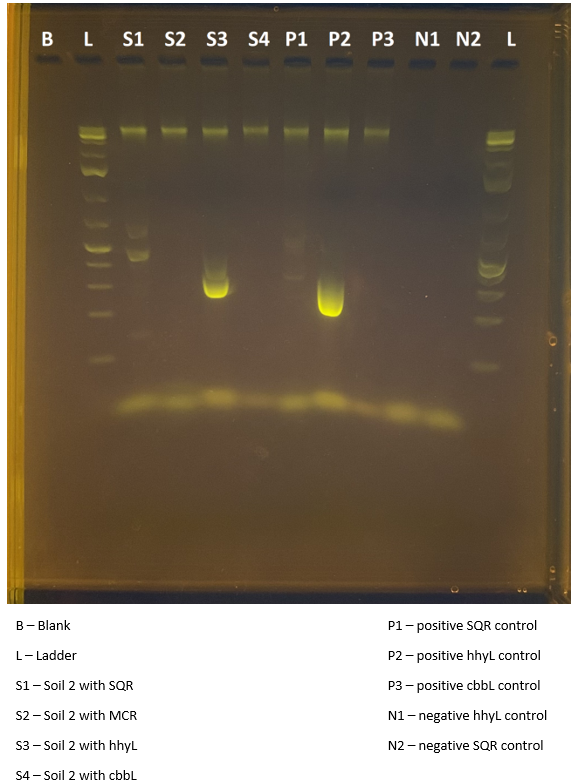
Image of an electrophoresis gel showing the results of a PCR test investigating the presence of functional genes in Soil 2. The positive result in S3 shows that the hhyL gene is present in the microbial community present in the soil sample.
Looking through the eyes of telescopes and exploring the wonders of our cosmos
Aditya Krishna Karigiri Madhusudhan (Crew Astronomer) and Peter Detterline (Director of MDRS Observatories)
The central objective is to formulate plans and effective strategies for the construction of an observatory for the upcoming Mars Science Analog Research station in India. A critical aspect of the observatory’s success is selecting the right telescope optimized for the weather conditions in India. Studies have been carried out to identify telescopes with optimal solar and deep sky observation capabilities. The telescopes are chosen such a way that they offer precision, high-resolution imaging, and compatibility with local weather patterns. To safeguard the chosen telescope and observation equipment, a weather-resistant dome is being designed using Fusion 360 software. The dome’s design is planned to incorporate features such as insulation, ventilation, and stability to ensure reliable and uninterrupted observations despite the weather conditions. To ensure the safety of astronauts during Mars missions, understanding and monitoring solar radiations is crucial. In addition to developing plans to build an observatory, the secondary objective is to make use of the Musk and robotic observatory, a specialized facility designed for solar and celestial object observations. I conducted photometric analyses of AG DRA to determine the variable star’s brightness. The star is observed to be much fainter than it should be. Hence further photometric measurements at various filters will be conducted. Several observations were carried out utilizing the MDRS WF robotic observatory to capture NGC 5904 (Globular cluster), NGC 281 (Pacman nebula), M51 (Whirlpool galaxy) and NGC 1952 (Crab Nebula). The following image is taken through the MDRS WF telescope, processed using AstroImageJ and Photoshop software.
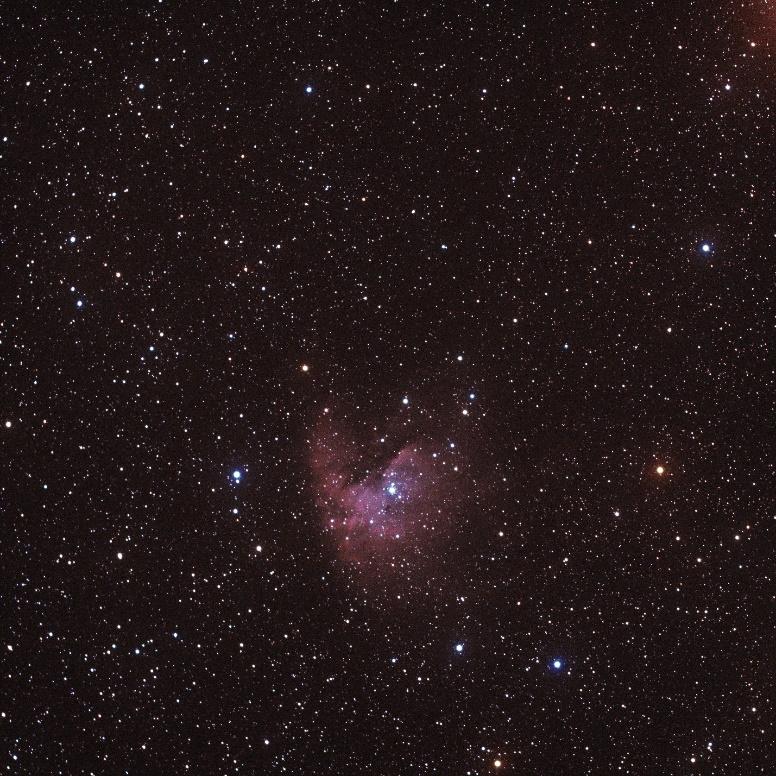

NGC 281, Pacman Nebula in the constellation of Cassiopeia, 9500 lightyears away (10-02-2024)
Propellant production at MDRS using water-bearing and carbonate rocks
Crew Engineer Rajvi Patel in collaboration with Crew 292 and Andrew Wheeler (291)
This project is focused on the production of rocket propellant methane utilizing the resources available on the Martian surface to make interplanetary travel self-sustainable. This mission included a collection of Gypsum (CaSO4.2H2O) samples and concretion samples as sources of water and carbon dioxide required to produce methane. Our goal is to determine a process to generate methane (CH4) from water (H2O) and carbon dioxide (CO2).
Three types of Gypsum samples were collected – efflorescent gypsum, authigenic bedded gypsum, and selenite gypsum. Preliminary analysis is required to be performed to validate if they release water at elevated temperatures.
Three types of concretion samples were collected as a part of EVA’s on this mission:
Type 1: Dark concretions in the dark matrix
Type 2: Light concretions in the light matrix
Type 3: Dark concretions in the light matrix
All three confirmed carbon dioxide release with vinegar.
As a part of future work, hydrogen can be produced from gypsum water using electrolysis. Hydrogen and Carbon Dioxide can be used to produce methane using the Sabatier process.
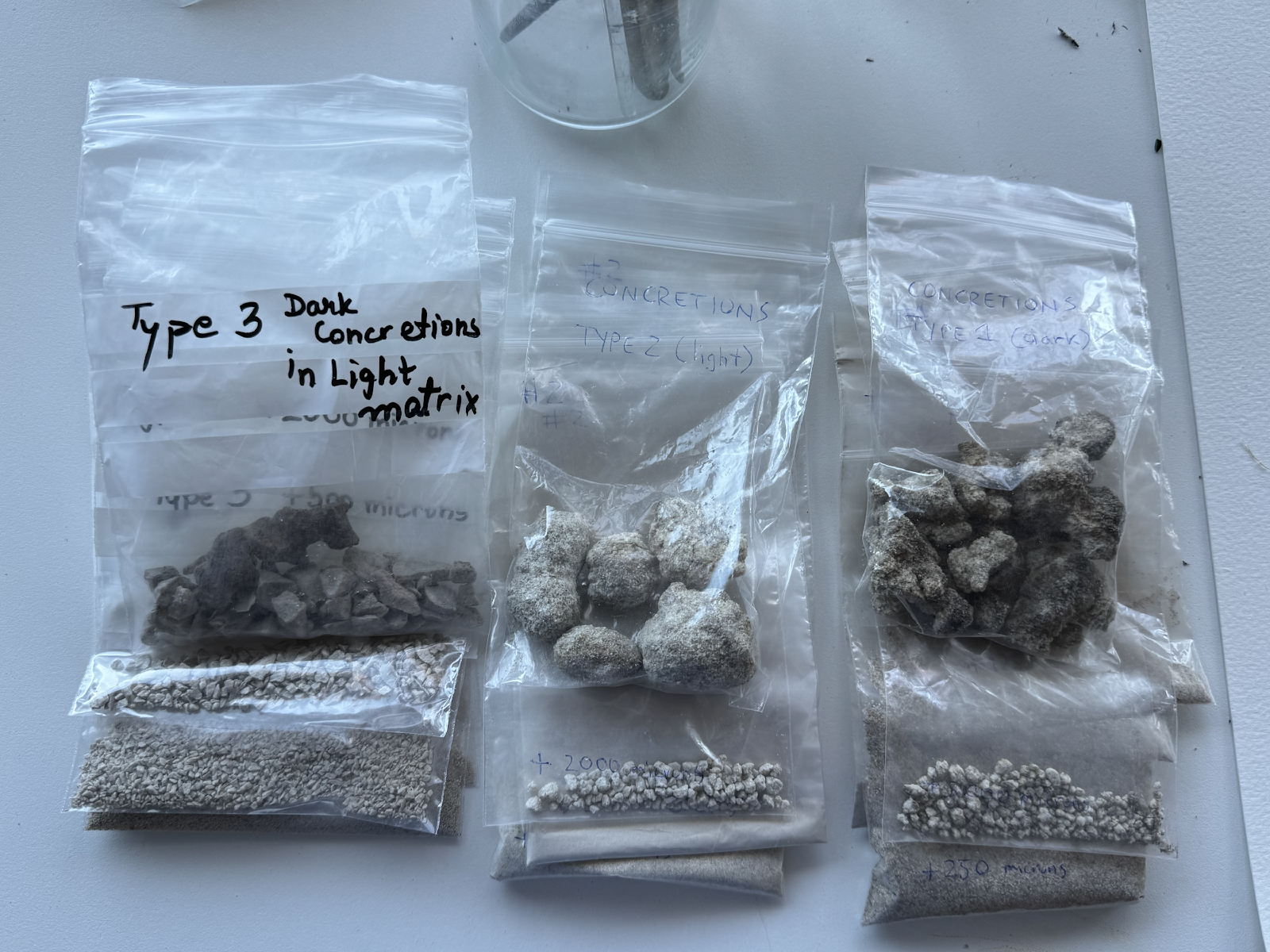

Figure 1: Types of Concretions validated for CO2 release
System requirements for the Ladakh station.
Rajvi Patel with the whole Crew 292.
This research includes the study of power systems, heating systems, and fuel systems at MDRS. The campus is powered by a 15kW solar panel system which feeds the 12kW battery bank. There is a 14kW propane generator that autostarts when the campus uses more power than the solar can provide. The main source of heat for the Hab is a forced air propane heater located above the shower room and bathroom. Hot water is produced from a 6-gallon propane RV water heater located above the rear airlock on the lower deck. There is a second wall-mounted ductless propane heater in case of low temperature or power outage. It has a propane heater and a wall-mounted cooler unit which provides cool air by using the evaporation of water across fans. It has a dual split heater/AC installed for the protection of the power system’s batteries. Propane for the Hab and GreenHab is in a 1000-gallon tank. This research is a basic study of these systems at MDRS. Future work will prepare a detailed systems for the station in Ladakh.
Crew 292 closes this mission report with a big thank you to everyone who has supported us.
On to Mars, Mangalyatri.
Dr. Annalea Beattie
Commander, MANGALYATRI,
Mars Desert Research Station, 16th February 2024













You must be logged in to post a comment.