[category science-report]
Mars Desert Research Station
Final Research Report
Crew 305 – Valles
Dec 8th, 2024 – Dec 21st, 2024
Crew Members:
Commander and GreenHab Officer: Hunter Vannier
Executive Officer and Crew Geologist: Ian Pamerleau
Crew Engineer: Spruha Vashi
Health and Safety Officer: Peter Zoss
Crew Journalist: Rashi Jain
Crew Scientist: Monish Lokhande

Research Projects:
1.
Title: Hydraulic Geometry of Ephemeral Streams to Potentially Elucidate Paleoclimate Author: Ian Pamerleau
Description, activities, and results: Ephemeral streams are present around the MDRS campus and carve out the landscape after heavy rain. The hydraulic geometry of these streams mathematically describes how the width and drainage area change as the flow moves up- to downstream. There is a range of values that the hydraulic geometry of rivers tends to fall within, which tells us more about climate, lithology, and sediment load. These values have been established for the more “mature” rivers with constantly flowing water.
However, the ephemeral streams at MDRS may not have achieved the values present in the literature. I will test if the ephemeral streams of MDRS hold the same hydraulic geometry in the literature, and if it is able to tell us anything about the climate.
We were able to thoroughly explore the three major areas where I wanted to take stream width measurements: Candor Chasma, Eos Chasma, and the region southeast of Kissing Camel Ridge (KCR). My objective was to take measurements of branching tributaries and between said tributaries along a main channel because the drainage area of a channel will substantially increase when the area of another stream is added. We also took three measurements of the stream width at each location a meter or so apart from one another to get an average width of the location.
I have not been able to create a plot of my data yet and am still in the processing stage. The trend I expect to see (i.e., smaller drainage area locations yield smaller stream widths and larger drainage area locations yield larger stream widths) will likely hold based on my observations and preliminary processing. The data may become a bit more complicated when comparing two sections of high drainage area, however, as there seemed to have been some variability in different factors such as lithology, slope, vegetation, etc.. I tried to limit these factors based on the location I chose but it is impossible to fully eliminate them, but I have taken photos of each location we took measurements of to better analyze any anomalies. I will hopefully be able to discuss these results with my undergraduate research advisor (whom I have worked on a geomorphology project with) or a geomorphologist/hydrologist at Purdue and share my findings at a conference once the analysis has been completed.
2.
Title: Effect of Variable Soil Moisture on Microgreen Growth
Author(s): Hunter Vannier
Description, activities, and results: Efficient plant growth is an important element of life at MDRS and will be critical for sustainability if we want to create a self-sustaining presence on other planetary bodies. For this project, I aimed to conduct an experiment that investigated how soil moisture content affects microgreen growth to find efficient watering practices. The established GreenHab infrastructure at the Mars Desert Research Station is an ideal place to conduct this experiment.
Experimental setup: I filled four 3” x 3” potting containers with Miracle Grow potting soil available in the GreenHab. The soil required priming and mixing with water, so the pots started out with some moisture level. In each of the pots, I added 1 g of broccoli microgreen seeds, then covered with a thin layer of soil. Each morning, I would water each pot with a specific quantity of water. Pot 1 received 2 oz water, Pot 2 received 1.5 oz water, Pot 3 received 1 oz water, and Pot 4 received 0.5 oz water. Pot 5 was a control pot and received no water over the duration of the experiment to determine if the ambient moisture conditions in the GreenHab were sufficient to stimulate growth without watering. The soil moisture monitoring system consisted of four capacitive soil moisture sensors (one for each pot) attached to an Arduino Uno R3 microcomputer (Fig. 1). Two measurements were taken in the morning, one prior to watering and one after, and one measurement was taken in the evening via direct connection to a personal laptop while running an Arduino serial monitor code. An initial baseline reading for each was obtained a day after the soil was primed
(prior to seeding). I waited a day after priming to equilibrate the moisture content for each pot. Subsequent measurements were subtracted from these base values for the respective pots.

Figure 1: The soil moisture monitoring setup. The Arduino Uno is shown in the bottom left of the image, and soil moisture sensors are shown in each pot, labelled 1-4. The image is from the final afternoon of the experiment, December 20. One can see how similar the microgreen growth is in Pots 1-3 despite receiving significantly different water quantities. .
Results from the experiment are shown in Fig. 2. The first day of watering occurred on December 16. Initially, each pot was near the baseline value after the first watering except Pot 1 (2 oz). The 2 oz of water may have been sufficient to saturate more of the soil compared to the other pots. However, by the evening the pots had once again equilibrated. On the morning of Day 2, a sinusoidal pattern developed that persisted for the duration of the experiment, but the moisture of each pot seemed to reach a stable pattern on Day 3 (December 18). Pot 1 (2 oz) displayed the most significant change in soil moisture between morning watering and evening, and it maintained consistently higher soil moisture content than Pots 2-4. Interestingly, the pots ranging from 0.5 to 1.5 oz tend to have somewhat similar soil moisture content, each significantly lower than Pot 1 (2 oz). Pot 4 (0.5 oz) often has a higher soil moisture content than Pots 2 and 3, which is unexpected and may be due to a higher concentration of water being deposited near the sensor when watering, or a slightly different sensor depth. In general, the pots lose moisture at a relatively constant rate during the day and evening. Based on the sensor data alone, it seems that 0.5-1.5 oz of water could achieve similar soil moisture. However, most of the moisture could have remained in the top few cm of soil for Pots 2-4. This is in contrast with Pot 1 (2 oz) where water seemed to consistently saturate more of the soil and to a higher degree. This is an important result because microgreens have shallow roots and can be sustained by soil
moisture content at the surface rather than at depth. Therefore, I conclude that 2 oz of watering for these pots is more than needed to grow the microgreens.
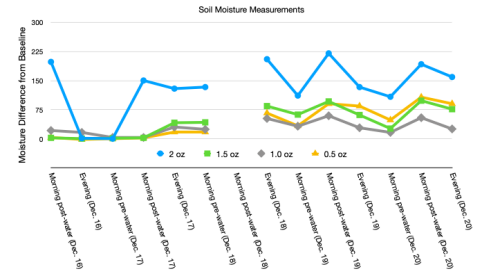
Figure 2: Sensor data from the soil moisture monitoring station. The y-axis shows soil moisture values, and the x-axis shows the time of day when measurements were taken. Each colored line represents one of the pots: blue is Pot 1 (2 oz), Pot 2 is green (1.5 oz), grey is Pot 3 (1 oz), and Pot 4 (0.5 oz) is orange. There is a gap because data was not obtained for the Dec. 18 post water measurement.
This assertion is supported by observational evidence of microgreen growth (Fig. 1). The microgreens were first observed to sprout on the evening of December 19. Pot 1 (2 oz) clearly had 4 to 5 times the growth observed in Pot 2 (1.5 oz) and Pot 3 (1 oz). By the morning of December 20, Pots 1-3 clearly had microgreens occupying most of the pot; Pots 2 and 3 had similar amounts of microgreens, and about ¾ that of Pot 1. Pot 4 showed signs of soil disturbance caused by sprouting but the microgreens had not penetrated the surface of the soil. Based on the observed growth rates and soil moisture content, I conclude that 1 oz of water per pot is the most efficient watering practice for the broccoli microgreens. Pot 3 (1 oz) achieved a similar growth rate as Pot 2 (1.5 oz), and though it did not sprout as quickly as Pot 1 (2 oz), a similar level of growth was achieved by the end of the experiment with half the amount of water. A future experiment could be to first saturate each pot with variable amounts of water, then add a similar amount of water to each to see if a larger initial watering could stimulate growth and enable less subsequent watering.
To translate these results to the GreenHab, we can compare the pots to the raised beds that can be used for microgreen growth. The beds are 33.5”x 13” for a total surface area of 435.5 in2 and the pots are 3”x 3” for a surface area of 9 in2. Assuming the same depth, this means ~50 pots would fit in the raised bed, and that to efficiently water the bed it would take 50 oz per day. Throughout my time at MDRS, I have been using at least ~64 oz of water per day for one of these beds and sometimes an additional 30 oz. At minimum, my experiment supports that I could improve efficiency in raised bed watering by ~22%, a significant improvement. I would recommend 50 oz per day for future crews growing microgreens in raised beds. There may be changes in evaporative rates between the beds and pots which should either be calculated or tested.
3.
Title: Sampling Paleosol Sequences for Mars Comparison
Author(s): Hunter Vannier
Description, activities, and results: The goal of this project was to collect samples from at least one exposed paleosol sequence with the intention of bringing it back to Purdue University for spectral and microscopic analyses. Paleosols have been proposed to have been observed on Mars via rover data, and little work has been done to understand their role in sedimentary recycling and retention of past water on the Mars surface. Three paleosol sequences were collected (15 total samples) that represent tens of millions of years of history in the MDRS region. The first two sets were collected on Sol 3 in the interior and just outside Candor Chasma (Fig. 3). The third was collected near Zubrin’s head. Complimentary to the Crew Geologist’s work, river channel sediments were also collected at different locations across MDRS (7 total) with the aim of understanding how paleosols are recycled in the fluvial systems at MDRS, and how composition changes spatially across the field areas.
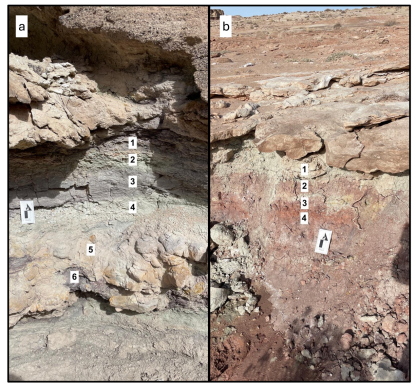 Figure 3: Example paleosol exposures observed during EVA 03 in Candor Chasma. Numbers indicate sampling locations within the paleosol sequence. (a) Paleosol sequence ~300 m after the entrance to Candor Chasma. Darker-toned layers indicate higher concentrations of organic material and are consistent with changing water environment. Capping rock is a
Figure 3: Example paleosol exposures observed during EVA 03 in Candor Chasma. Numbers indicate sampling locations within the paleosol sequence. (a) Paleosol sequence ~300 m after the entrance to Candor Chasma. Darker-toned layers indicate higher concentrations of organic material and are consistent with changing water environment. Capping rock is a
conglomerate and sandstone of the Morrison Formation (b) Paleosol sequence just exterior to the Candor Chasma entrance. Note the significant amount of red color compared to (a), indicating a much higher concentration of iron oxides. Cap rock is a fine-grained sandstone that is commonly exposed at ground level through the Compass Rock area.
The samples collected at MDRS will be analyzed in the pursuit of improving our understanding of paleosols on Mars and their relationship to variable climates on Mars. Visible to near infrared spectra, X-Ray fluorescence, and X-Ray diffraction data will be collected to form a preliminary data set to improve context for Mars observations. This data will likely be published at a conference in the next year. This data will also be the basis for a future NASA Solar Systems Working proposal to investigate the MDRS paleosols and river systems in greater detail.
BONUS: we came across sedimentary concretions that are documented in the MDRS Geology Unofficial Handbook. These are very similar to outcrops recently observed in Jezero Crater by the Mars 2020 Rover. See Figure 4 for a comparison.
a
c
 b d
b d
Figure 4: Comparison between concretions at MDRS and on Mars. (a,b) Sandstone concretions in the fluvial channel near Zubrin’s Head. (b,c) Concretions observed by the Mars 2020 Perseverance Rover in Jezero Crater near the Bright Angel formation around Sol 1022 (Courtesy Adrian Broz; publicly available images from Mastcam-Z).
4.
Title: Investigating Rover Applications in a Mars Analog Environment
Author(s): Spruha Vashi
Description, activities, and results: The objective of this work was to build a modular rover that can traverse the analog Mars terrain along with crew members on EVA. Testing at MDRS was set to include mobility testing over different sections of terrain, confirming communications and operability, and exploring human-machine teaming capabilities. However, after multiple long days of group efforts at assembly and troubleshooting, the rover, named Hermes, was unfortunately unable to start and be ready for data collection, but is pictured in Figure 5. While this outcome was unfortunate and meant that Hermes could not be tested outside on EVAs, it provided a good insight into major improvements in assembly that can be applied for future testing. Understanding the complex system and its weakest points of failure was not lost, and this information now allows us to ensure a smoother assembly process in future usage.

Figure 5: Hermes the rover, with electronics and wiring included. Expected weight is 25 pounds, and expected maximum speed is 1.6 meters per second.
Although Hermes was not utilized on EVA, data and observations were still collected to help understand applications of rovers in the analog environment, especially in scenarios where the rover would act as a member of the EVA team. Some main points of investigation were mobility, functionality, communications, teaming strategies, and future design. For mobility, a single tire was taken out on EVA and tested on multiple different terrain types to understand its ability to travel across different terrain. Since the Crew Geologist’s research was primarily working with stream beds, most terrain testing was conducted on or near stream beds to understand the scenario in which the rover would be travelling along with the team while collecting stream bed data. The testing was done by rolling the single tire across 10ft strips of terrain multiple times, with the same downward pressure applied while rolling to simulate the actual rover’s 25lb weight, as seen in Figure 6. The results showed no more than 5 mm of tread depth in the softest terrain tested, compared to 200 mm footprints. In stream beds, the tires showed a clear tread but when hitting denser patches required more effort to get past. On dry and rocky lands, the tires showed no tread but rolled smoothly over different sizes of small rocks. It is still uncertain and unlikely that the rover would be able to traverse across very rocky, winding paths.

Fig. 6: Image of terrain testing in a stream bed. Three strips of 10ft were identified and marked with flags and the tire was rolled along all three. Tire tracks are seen at each line, note that the found was denser in the center line and thus there are gaps of tracking since the tire slipped at those points.
To understand the functionality and teaming strategies that the rover could possibly adopt once it is functional, qualitative observations were made on certain aspects of data collection that delay operations and could be eliminated with the presence of a rover. For example, it was observed during the Crew Geologist’s stream bed measurements that the travel bag of materials is a hindrance to carry. It was noticed that writing down geological information, data points, and GPS information all takes time, and some of these items can be noted down by an autonomous system that is present, in this case, a rover. On EVA 11, the Crew Geologist was timed while he was taking measurements to understand his efficiency and points of improvement. On average, there was a reduction of about 1 minute of time from the Crew Geologist taking the measurement entirely by himself vs. having an EVA team member help with the measurement. While this confirms the idea that an EVA team will make data collection more efficient, the important note is that regardless of the number of members involved, data recording took 30-45 seconds for every measurement. Data recording was assumed to include notes on geological information, data points, and GPS information. All these items can be autonomized with a rover on hand that can collect and store the data and simplify the measurement process for the crew members. Another point of investigation was the time it takes for the rover to travel alongside a crew member. The specifications of Hermes indicate that its maximum speed would be about 1.6 meters per second, or approximately 3.5 miles per hour. Although Hermes was not actively tested, a measurement was made of comparing a crew member traveling from one data collection point to another at normal walking speed vs a crew member walking at specifically 3.5 mph (estimated to be 2 strides per second). The delay of a travelling rover was found to be 31 seconds and would also be further delayed in the case that the stream bed is very rocky, meaning it must travel on the outside, flatter areas.
The observations made on EVAs clarify future design upgrades of the rover. For example, communications and data recording capabilities, as well as carrying capacities would be the most ideal additions to Hermes at the time. It is hoped that with future usage of Hermes, more scientific applications can be implemented, and the rover can be well versed to work with many different variations of data collection and support the
crew’s research ambitions. Future observations of Hermes in action working in a team of scientists can further identify failure and improvement points for teaming strategies of autonomous systems and astronauts in analog environments, the Moon, Mars, and beyond.
5.
Title: MDRS Monitoring Overlay Sensors
Author(s): Monish Lokhande
Description, activities, and results:
Description: The project was focused on developing a network of Raspberry Pisto measure data from various locations in the habitat to measure the necessary sensor data (CO2, VOC, Air Quality, Temperature and Humidity). This data would be collected and analysed for any possible sudden changes. The “Sensor Packs” would be made to operate independently on batteries.
Activities: A total of two sensor packs were developed inhouse were placed in GreenHab and Lower Hab to continuously monitor the temperature, humidity and CO2 levels. The sensor packs relay the information in the two different types of feeds: Local and Global. The local feed updates every minute to provide real-time data to the crew members in the habitat and can be used by the local crew members to monitor the health of a certain location in the hab. On the other hand, global feed is used as a transfer of necessary information to a remote ground station. The feed is designed in such a way that it considers the delays inherent in Mars-to Earth communication. To limit the consumption of bandwidth and latency effects, the global feed by default parses the data and sends only the necessary data at regular intervals when everything seems within acceptable range of values. The continuous relay of data for global feed is done when there is a sensors which is not functioning or has faulty values. The sensor modules have the dual functionality to power using battery packs or by a wall power source. This makes it possible to be located at any location in the habitat.
Limitations: The sensor modules had a limitation on the number of sensors because of limitation of data to be published. The CO2 sensors needed calibration to have a reference for correct value calculation and therefore the values had a higher fluctuation.
Results: The sensor modules developed actively monitor data from the GreenHab and Lower Hab successfully. The local dashboard image is given as a reference, which populates with data every minute. If
any sensor has faulty data, there is a corresponding notification sent to the local and global dashboards. Having local and global dashboards help crew members quickly analyse any faults as well as inform the remote ground station of any anomalies that might have occurred. Future applications will include adding a notification in the form of sound or LEDs, to alert which sensors are not working or giving not acceptable values. Another extension will be to include more sensors. The project is being continued by Crew 306 for their research.
Figure 7a. Local Data Feeds for individual sensors
 Figure 7b. Local Dashboard for sensor information
Figure 7b. Local Dashboard for sensor information
6.
Title: Safety Lessons and Design Requirements on Autonomy for future Martian Habitats Author(s): Rashi Jain
Description, activities, and results:
Description: Mars will have both periods of dormancy and crewed operations. Therefore, future Martian habitats must integrate autonomous systems and design practices that ensure reliable and safe operations in both operational phases of the Hab. The objective of my study is to understand how the different systems work together in a Habitat, identify weak design points and practices, and recommend safety controls and design requirements for future autonomous systems that can ensure both quick decision-making and resilient and safe habitat operations.
Activity: For this, I am studying MDRS habitat design and operations during the 12 Sols that we have at the Mars Desert Research Station from December 8th, 2024 – December 20th, 2024 to: (i) identify and draw out the functional relations between different systems in the Habitat, (ii) analyze how effective are the Habitat systems at maintaining or providing resilience to the anomalies and faults that we face during the mission.
Results: In this report, I include the results from Sol 1 – Sol 6 operations. I am still working on processing the data from the remaining six sols. For Hab, I include results only from Science Dome and the EVA operations. I am still working on processing observations made in the Main Dome, Green Hab, Repair and Maintenance Module, the Tunnels, and the Airlock.
Habitat Design
I toured each section of the Habitat and documented the different design features and resources available in each of those sections. The purpose for this exercise in each Habitat section is to understand the different resources available in each dome and what they enable us to do. It helps us (i) analyze how can or can the equipment and resources available to us both locally in each dome, and throughout the Habitat help us navigate anomalous situations, and (ii) are the current design and resources adequate to interface with autonomous systems? What, if any, should be the design requirements for future robotics or autonomous systems?
This step led to Habitat Systems Functional Relations
Habitat Systems Functional Relations
Relations between different habitat systems at MDRS. The different systems in the Habitat can be categorized into the following seven: power; interior environment; environmental control, life support system, and extra-vehicular activity, food processing, structure, command, control, and communication; and human, robots/safety controls. Here we show only power, but during the time at MDRS these models have also been sketched out for extra-vehicular activity, interior-environment, and command, control, and communication. I am still working on putting together models for other systems listed.
Power System: Figure 8 shows the power system component architecture and relations at the MDRS facility. There are two main sources of power, the solar panels (primary source) that are supposed to generate power and charge the batteries during daylight, and the backup generator (secondary source) that is to provide electricity in case solar panels malfunction, or the batteries run out of charge. Power generated through solar arrays, or the generator goes through a Sequential Shunt Unit integrated within the system which regulates the voltage of generated power. It then goes through a Direct Current Switching Unit (DCSU) which is the first component in the power distribution system. The DCSU determines power flow: i.e. how the power is distributed based on power generated and the integrated algorithm. DCSU interfaces with the batteries using a Battery Charge Discharge Unit (BCDU), whereas it interacts with the downstream loads using Main Bus Switching Unit (MBSU), DC to DC converter unit, that converts voltage to 120 Vdc, and Remote Power Controller Module (tripper box).
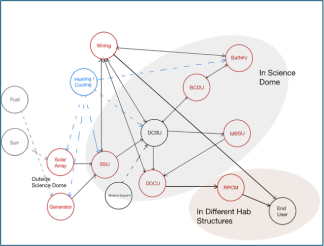
Figure 8: Power System Component Architecture and Relations at MDRS
With this power system component architecture and relation diagram at MDRS, we built a functionality diagram for individual components. Functionality diagrams are causal relation diagrams that show what the function of each component in the system is and what are the different factors it’s affected by. Figure 9 shows the functionality diagram of the solar panels. The grey circle represents the component itself (solar panel), the blue circle represents the function (generate power), the black circles represent the other systems in the Habitat system that affect either the component or its function (in this case we see that solar panel functions are affected by heating/cooling systems), the yellow circles represent variables and any other factors that influence the component’s function (in this case the solar irradiance affecting the power generative capacity).
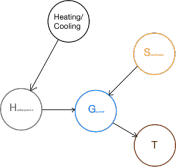
Figure 9: Functionality diagram for Solar Panels
Using these functionality diagrams, we place “T” variables, also known as test variables. These T variables inform the design of where future monitoring systems should be placed. For instance, in case of a solar power, we recommend placing the
Operations summary: I monitored Hab operations, resources usage, and supplies through the 12 Sols and organized the data collected in an Excel sheet.
I use insights from Habitat Design, Systems Functional Relations, and Operations to establish Safety Lessons, and Design Requirements on Autonomy for Future Martian Habitats:
Safety Lessons:
1. Generate in-situ resources: With limited availability of resources available within the Habitat on Mars, we will need to generate in-situ resources. This includes water, oxygen, and fuel reserves. While Crew 305, did not conduct any experiment on in-situ resources: this should be a requirement for future crews as all long-duration mission to Mars will require the crew to become self
sustainable.
2. Make the most of available sources: Mars receives less than half the solar irradiance (590 W/m2) we receive on Earth, therefore every W of power generated here on Earth will have to be adjusted to what will be generated on Mars. It will be important to make the most of the resources available. For solar power, one can add solar concentrators and a controller that rotates the solar panels with solar position, like what happens at ISS.
3. Have a reliable source of reading for the sensors and water tank level: Our crew had two sources of water readings: one from the sensors at Hab, and the other that we got from our calculations. For the six sols I accounted for, the numbers differed anywhere 3.22 gallons – 37.855 gallons. We went with the more conservative estimate to estimate the remaining amount of water available to us. Given the scarcity of resources however, it is advisable to know exactly the amount of resource you have, and a margin of safety to it, than either under-estimate or overestimate.
4. Take an active effort at bringing the systems back to nominal operating conditions as soon as possible. Crew 305 Valles entered the Sim with no solar panel batteries non-functional (the Battery Charge Discharge Unit was broken, as a result of which, the batteries could not store power). This resulted in the crew using solar power in the day as the main source of energy during the day and the backup generator as the main source of energy during the night. In case one or the other failed, the crew would be left without power, which is essential to keep all critical systems running on Martian habitats.
5. Have magnetic self-aligned helmets on EVA suits. While we were a crew of six, with three people going on EVA and three people staying back to help with EVA operations, initial missions on Mars can have a lot of unexpected situations. For e.g. need for a rescue mission, only one person in the EVA/airlock module. It is important that while each crew member has help, they are also independent and able to wear their own space suit with minimal help from the others. One big problem with the two piece suits is the alignment of the helmet
6. Have multiple ports of exit: Cabin depressurization is a big cause of concern on extra-terrestrial habitats, both on Mars and especially on the Moon. In case of cabin depressurization, sections of the Hab will be isolated using airlocks. When this happens it is still imperative that people in other sections of the Habitat are able to safely exit the Hab. While it is not possible to have all EVA equipment in all Hab modules, it is important to limit the number of people in domes at one time and have the adequate number of EVA equipment and an exit airlock in each module.
7. Check for consistency in equipment performance: For the first six EVAs, I calculated the drop in percentage per mile travelled by the rovers (see Table 1). We see that the rovers perform better at preserving battery for longer distances than they do for shorter EVAs.
Table 2: Drop in Percentage per Mile of Rovers for the First Six EVAs.
|
|
Drop in percentage per mile travelled. |
|
Miles |
Curiosity |
Perseverance |
Opportunity |
Spirit |
|
EVA 1 |
0.55 |
20 |
10.90909091 |
|
|
|
EVA 2 |
0.55 |
|
|
10.90909091 |
9.09090909 |
|
EVA 3 |
3 |
|
|
8 |
3.33333333 |
|
EVA 4 |
7.45 |
4.02684564 |
4.966442953 |
|
|
|
EVA 5 |
5.54 |
|
|
6.137184116 |
5.77617329 |
|
EVA 6 |
8.22 |
|
4.501216545 |
|
4.62287105 |
We can use this information to keep track of rover performance, and confidently estimate how much each individual rover can travel before it runs out of charge. Long term tracking of rover’s performance will also help astronauts determine whether a rover needs earlier maintenance or not.
8. Install methods for investigating software bugs: Crew 305 Valles used Astrolink to track the GPS coordinates of the crew while they are out on EVA. On one of the EVAs, the Astrolink software showed four trackers out instead of three. The Hab comms team communicated with the EVA crew if they had an extra-tracker (Astrolink 10) on them. Upon receiving a negative, the crew with the Mission Support established that Astrolink 10 was a digital artifact. Situations like these, however, would get increasingly confusing with a larger / independent crew. It is important to have methods for investigating software bugs (evaluating what the root cause is) like these and addressing them.
9. Practice concise comms: Currently, aviation pilots use very precise language to communicate with other pilots and the Air Traffic Controller. It is important to establish similar rules for communication
over comms such that everyone is heard clearly without any misinterpretation. Crew 305 progressively improved in their communication while in the Sim.
10. Understand your systems well: It took a while for Crew 305 to realize that the rovers read the total number of hours they have been operational rather than remaining range on the full charge. While the crew was able to accurately figure out in time what the rover reading said (and fortunately it did not lead to any accidents), it is important for the crew to understand the systems they are working with well – to avoid any mis-interpretations that could lead to mishandling data or equipment.
Design Requirements on Autonomy for future Martian Habitats:
1. Add following monitoring systems and add remote access to them in each Hab area. a. Battery charges
b. Power Generated by Solar Panels
c. Temperature Sensors for Generators and Fuel Cells
d. Voltmeters for Sequential Shunt Units
Our functionality models for the power systems revealed that it is important to have the following sensors to track performance of the power systems at any given time. The readings can be output to the Main Dome Computer Unit that tracks all other systems. This is important for both equipment performance tracking and smooth autonomous system integration.
2. Have a running inventory of the Hab and the different resources available.
3. Automate system transitions: 1) and 2) will allow smooth automated system transitions. While the MDRS has very active Mission Support to facilitate these transitions, Mars is not going to have Mission Support. Or the Mission Support will be 20 – 40 minute lag, and won’t be able to provide on-site services.
4. Have functional back up devices, that are structurally non-redundant: During the power outage, the Main Dome in Crew 305 relied on an igniter heater that did not rely on the electricity, but instead on propane. This kept the crew warm, even when the electric heating system didn’t work. This highlights that it is important to have back up devices that are functionally redundant, but not structurally redundant.
5. Organize resources and tools for ease of use: Figure 10 shows some of cabinet space organization in the Science Dome that house different equipment.


 Figure 10: Cabinet Organization in Science Dome
Figure 10: Cabinet Organization in Science Dome
While this setup is good for a human to work with. They will look around and find out what they need, it is too cumbersome for an autonomous system and will confuse them. Autonomous systems will need a cleaner organization to work efficiently. The best way to currently do this is to use a 3D printer, where you can create custom shelves and cabinets that autonomous systems can easily work around with.
Future work on this will include compiling a list of functionality models for all systems and components I documented at MDRS. These component functionality models will be used to create a digital extraterrestrial habitat model on the Control-Oriented Dynamic Computational Modeling Platform, where we can simulate different disruptions that will be present on Mars that cannot be simulated at MDRS either due to their absence (such as radiation) or for safety reasons.
7.
Title: Wearable-Based Autonomic Activity Profiles for Real-Time Cognitive Performance Monitoring in Spaceflight
Author(s): Peter Zoss
Description, activities, and results: This study will longitudinally quantify individual changes in autonomic nervous system (ANS) status via a wearable sensor in MDRS crew members to understand how our autonomic activity is associated with sequential measures of cognitive performance for predictive model development. Baseline data from the wearable devices will also be used to look at changes while living in analog isolation. The activities planned to be completed at MDRS included cognitive performance testing. This testing was scheduled to take place every other day starting from Sol 1 for a total of 6 testing sessions for each of the crew members.
This human factor project was able to get through all of its data collection period at MDRS. Cognitive performance testing has been completed for all crew members for the planned 6 tests at the MDRS. These tests occurred on Sols 1, 3, 5, 7, 9 and 11. The tests on Sol 3 had to end early due to power failure, resulting in an incomplete test for one crew member and a missed test for another. The cognitive performance test used is called the Cognition Test Battery, and it was administered to the crew via an iPad. The results from this research will be looked at further back in West Lafayette where analysis can be completed.


You must be logged in to post a comment.