[category science-report]
Commander: David Mateus
Executive Officer and Astronomer: Luis Díaz
Health and Safety Officer: Andrea De La Torre
Crew Engineer: Tomás Burroni
Green Hab Officer: Andrés Reina
Crew Journalist: Marina Buqueras
A team comprising individuals of Hispanic descent from various countries in Latin America, including Spain, undertook an expedition to the Mars Desert Research Station (MDRS). This venture holds critical significance, as it exemplifies the global nature of space exploration and marks a progressive stride toward diverse representation in astronautics. Integrating Hispanic individuals in such endeavors promotes inclusiveness and broadens the scope of talent, leveraging distinct insights and skills that varied backgrounds contribute. Additionally, this initiative acts as a beacon of motivation for traditionally underrepresented communities, spurring their participation in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) disciplines and human space flight, thus propelling innovation and reinforcing the enduring pursuit of interplanetary exploration.
Project 1: Early Fault Detection in Power Generator Systems
The continuity of the power supply in a Martian station is critical for crew survival. This preventive and predictive maintenance for all single-point failure components within the power generation system. This strategy seeks to detect and isolate possible faults before they cause unrecoverable failures. Focusing on the critical propane power generator at the Mars Desert Research Station (MDRS), we address the inherent challenges posed by constant vibration loads on combustion engines that degrade the parts over their lifetime. Leveraging a sensor kit comprising accelerometers and ultrasonic microphones, we capture and analyze the vibrations to construct a characteristic signature. Monitoring this signature over time enables early fault detection, providing timely alerts for necessary maintenance and preventing potential power outages.
The sensor kit was successfully placed in the generator during an Extra-Vehicular Activity (EVA). This allowed the engineer to assess their fine motor skills in full EVA suit. Subsequent nightly data collection, with minor interruptions due to now resolved software errors, facilitated data collection and analysis scripts debugging. Variations in sensor kit placement on the generator during the last two nights aimed to evaluate how the position impacts results. This analysis was necessary as the largest loads on the original position could exceed the sensors’ dynamic range.
The images below show the original placement of the sensor kit in the generator, and some preliminary results of the data analysis. Figure 1.4 in particular uses a digital peak detector on the microphone data and shows the frequency of bursts in the signal, i.e. loud short-lived noises. The pronounced deltas in that plot correspond to characteristic frequencies and harmonics of specific parts and assemblies. Knowing for example the rotation speed and number of balls in the bearings, one could easily identify which of these correspond to the bearing and therefore pinpoint changes in this graph to a specific issue.
While ongoing data analysis is imperative, this experiment validates the viability of integrating such sensor devices into critical systems, offering valuable insights into performance. The collected data establishes a baseline for the generator’s behavior, serving as a foundation for future failure detection and prediction with the potential installation of permanent sensors.
Project 2: Drone-Aided Martian Geolocation through Image Recognition
During the early stages of Martian settlements, the absence of a global navigation system akin to those on Earth requires the development of robust geolocation methods. These methods serve as vital backups to ensure the safe return of crewmembers to the base after exploration missions. This proposal addresses scenarios wherein a crew is stranded beyond the reach of a drone’s operational range, rendering autonomous search and rescue impractical.
Anticipating that the vicinities surrounding the base will be meticulously photographed and mapped by satellites pre-settlement, the crew should possess a database of georeferenced images. The proposed solution entails deploying a drone from the crew’s location to capture an aerial image of the site. Subsequently, an image recognition algorithm is employed to compare and match this drone-captured image with the existing satellite image database. This process facilitates the precise determination of the crew’s location and their relative orientation with respect to the station.
The image recognition script was developed in Python using OpenCV. The first step of the process is to detect the keypoints in both images and compute their descriptors with the Scale-Invariant Feature Transform (SIFT) algorithm. That is followed by the Brute-Force matcher to find the matches between both sets of keypoints, and Lowe’s ratio test to filter them. The next step is Homography, in which the optimal perspective transformation is calculated such that the error in the best matches is minimized. The final processing to estimate the position and heading uses the warp matrix returned by the homography step.
The first iteration of the image recognition script, designed to identify the drone image within the broader satellite imagery, underwent successful testing using data gathered during Extra-Vehicular Activities (EVAs) at the Mars Desert Research Station (MDRS). The dataset comprises observations from two EVAs to Candor Chasma, one to El Dorado Canyon, one to Tharsis Montes, and one to Hab Ridge, offering diverse landscapes and lighting conditions at various times of the day to assess the robustness of the algorithm. The reference satellite images were sourced from Google Earth.
Illustrated below is an example of the algorithm’s functionality in aligning the drone image with the corresponding satellite image. Figures 2.1 and 2.2 depict the original images, while figures 2.3 and 2.4 showcase the outcomes of the processing algorithm. In Figure 2.3, the images are side by side, the drone image on the left has an arrow indicating North, and the satellite image is on the right. Green lines connect the matched keypoints between the two images. Given Mars’s lack of a uniform magnetic field for determining direction, accurate calculation of the North direction is critical for heading estimation. Figure 2.4 demonstrates the superimposition of the two images, validating the algorithm’s accurate matching and warping of the drone image. Additionally, an arrow denotes the original heading of the drone.
The primary objective of this project has been accomplished with success, affirming the efficacy of the proposed tool. Looking ahead, the subsequent phases entail the formulation of metrics aimed at quantifying the precision of the calculated fit. This leads to the implementation of an optimization algorithm to fine-tune the input parameters. This progression marks an important step towards enhancing the overall robustness and reliability of the geolocation method, ensuring its efficacy in different terrains and contributing to the safety and navigation protocols for future settlements.
Project 3: Drone search and rescue
In order to ensure the safety and effective rescue of crews facing critical situations on Mars, it is essential to enhance exploration methods and implement reliable contingency plans. Our proposed solution addresses potential issues such as crew members getting lost or trapped, or the need for alternative routes due to unforeseen obstacles. We advocate utilizing drones for crew searches and facilitating communication between the base and the crew. By incorporating drone technology, we can ensure efficient and safe exploration, even in remote and hazardous areas.
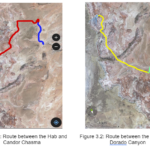
Our successful trials at the Mars Desert Research Station (MDRS) demonstrate the feasibility of utilizing drones for crew searches. Notably, the captured aerial images provide compelling evidence of their effectiveness. Moreover, our experiments have shown that drones can effectively navigate the Martian terrain, providing alternative routes to the crew during emergency situations like landslides. We have confirmed that both manual and automatic drone control modes are viable options, catering to the specific needs of different scenarios.
By utilizing GPS points and coordinates expressed in latitude and longitude, we have successfully charted safe routes for navigation. These coordinates were obtained through GPS waypoints and validated using Google Earth and QField during our exploration missions to Candor Chasma, El Dorado, and Hab Ridge. Examples of these routes are shown in figures 3.1 and 3.2. Figure 3.3 shows an image of the crew during an EVA taken by the drone sent from the Hab.
The incorporation of drone technology for crew searches and the delivery of alternative routes in Martian environments represents a critical step towards enhancing the safety and security of future settlements on the Red Planet.
Project 4: Building materials for future Mars civilizations
The construction of infrastructure in space poses significant economic and technical challenges, making it imperative for future space missions to rely on simple and readily available materials for astronauts. During our stay at MDRS, a construction materials project was conducted for future civilizations, guided by studies from the University of Manchester indicating that combining Martian soil with basic materials such as starch and water can produce highly resilient concrete for use in upcoming missions. In an article published in the Open Engineering journal, they demonstrated that starch can act as a binder when mixed with simulated Martian dust, resulting in a material with properties akin to concrete.
To verify this, soil samples were collected from various areas around MDRS, as their chemical and mineralogical content closely resembles that of Mars. These samples were then combined with homemade rice starch to act as a binder when mixed with simulated Martian dust, resulting in a material with similar properties to concrete.
The rice starch was initially prepared as follows:
- 500 g of rice were soaked in water overnight.
- The water was discarded, and the rice was washed.
- The rice was blended with 150 ml of water.
- The resulting mixture was placed on filter paper to remove excess water.
- Once the mixture dried, it was baked at 50°C for 1 hour.
- The dried mixture was ground in a mortar and sifted using a 125-micron sieve.
- Once the starch is ready, each sample is sieved using the 125-micron sieve until 100 g of each sifted sample is obtained.
Sample number 1 was collected from Marble Ritual, at coordinates (UTM 518606,4251022), and is a whitish sample, indicating the presence of gypsum and calcium.
Sample number 2 was obtained from Marble Ritual at coordinates (518684.50, 4250937.20). The sample exhibits the presence of clods, with a mix of medium, small, and fine particles. The soil comprises approximately 50% of dense, firm clods and friable, fine aggregates. Its reddish color suggests a high iron oxide content.
Sample number 3 was taken around the HAB in front of the ScienceDome with coordinates (518204.30, 4250908.40). It consists of reddish-brown clays and shales, reddish-brown sandstones, and cemented nodules of anhydrite or carbonate, exhibiting cracking clays. In the MDRS field area, montmorillonite and nontronite clays are mostly oxidized, lacking diagenetic pyrite. Erosion has led to limited formation of large, clear fragments of regolith gypsum.

Sample number 4 was taken at Candor Chasma at coordinates (UTM 520500,4251000). It consists of thin-bedded red-brown shales with beds of nodular gypsum and cross-cutting gypsum veins. Its color suggests a low iron oxide content.
Sample number 5 was taken within the Dorado Canyon at coordinates (UTM 519371, 4248609). This sample contains very moist sand with coarse grains, rich in minerals, as it was collected from what appeared to be a water deposit. This type of soil terrain is typical in canyons.
Sample number 6 was collected in Candor Chasma at coordinates (UTM 520920,4251060), and it consists of clayey sand that readily absorbs water, with a lower quantity of iron oxide.
A pH test was conducted on all samples, and the results ranged between 4 and 5, indicating that the soil was acidic.
The process for creating the concrete bricks was as follows:
5.90 g of starch, 100 g of soil, and 25 ml of water were combined. Subsequently, the mixture was placed in a mold and microwaved with a glass of water for 3 minutes and 30 seconds for its initial drying. Finally, it was oven-dried and hardened at 125º C for 4 hours. Once the time was completed, the Martian concrete brick was removed from the mold and deemed ready. The same procedure was repeated for each of the samples.
Results
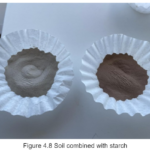
Several concrete bricks were obtained, each crafted from one of the samples, as depicted in the following images:
As can be observed, the majority of the samples resulted in resilient concrete, except for sample number 2, which broke upon exiting the oven, and sample number 5, which, due to its characteristics, was impossible to create. The best concrete samples were 1 and 4, exhibiting notable strength upon touch.
The study of the concrete samples will continue in Mexico, where further tests on strength, hardness, compression, and rebound hammer, among others, will be conducted.
In conclusion, the characteristics of the MDRS soil are suitable for creating construction materials using simple and readily available ingredients. The combination of simulated Martian dust, starch, and water has proven to produce a robust material with properties akin to conventional concrete. This innovative approach can potentially simplify and reduce the cost of future space missions, paving the way for infrastructure construction on the red planet.
Project 5: Methodology for the Characterization of the Social Implications of Confinement and Isolation in Analog Martian Missions: A Theoretical Approach
With the aim of conducting a sociological and anthropological analysis of the written material, the approach to the ethnographic immersion was based on the conceptualizations of Émile Durkheim and Michel Foucault regarding the sacred and the profane and power-knowledge relationships, respectively. These theoretical perspectives were considered relevant as they explain essential elements that gain significant meaning in the review of "everyday" processes, and through their review and understanding in the context of analogous missions, they allow for the consolidation of approaches on how upcoming processes these factors must be considered essential in reviewing the success or failure of a mission. Moreover, in long-term space travel projects they will provide insight into how norms, laws, hierarchies, punishment systems, and various elements that contribute to the organization of human groups in extraplanetary scenarios may be established.
The construction of such categories occurred as patterns of regularities and singularities in the rutine of the crew could be identified. Considering the differences and similarities in the composition team according to the origin of the participants, their professions, their affinity for each other, mission objectives, and other diverse factors, we established that the study of social processes within these scenarios could be conducted using basic cross-cutting variables that organize what occurred within a specific reference framework identified by us.
Accordingly, the categorization exercise was carried out through the establishment of two essential elements present during the mission, which will be called basic categories, which are in turn detailed in light of seven specific variables that will be placed as subcategories, as they are encompassed in the definitions of a larger set. Thus, the scheme of variables used for analysis can be presented as follows:
• Basic category: group cohesion.
o Subcategories: unofficial activities; adverse situations.
• Basic category: sacred-profane.
o Subcategory: ritual; routine; celebration-festivity; normativity; symbolic.
The categorization of social processes into basic and subcategories has proven to be a robust analytical framework, particularly effective in the context of space missions, which are akin to high-stakes, isolated societies. The variables identified – including unofficial activities, adverse situations, rituals, routines, celebrations, normativity, and symbolic elements – serve as fundamental building blocks for understanding and shaping the social fabric of long-term space travel.
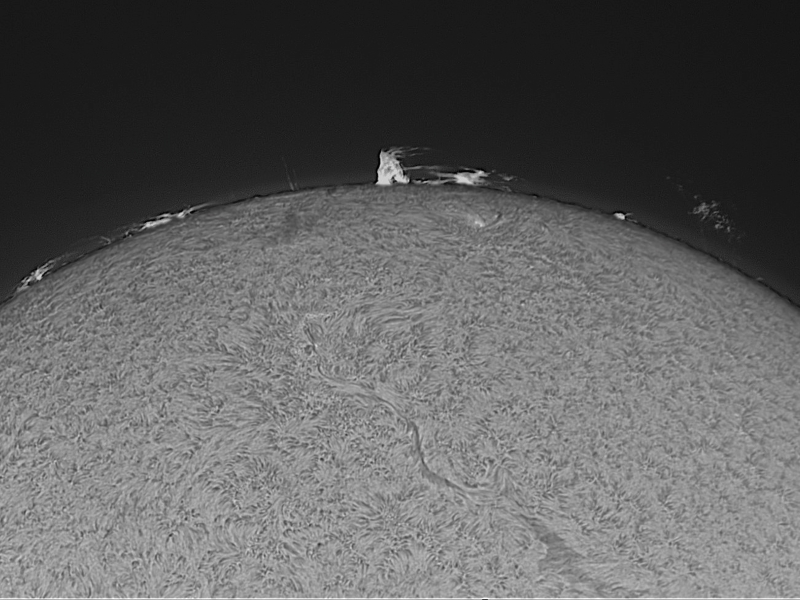
Project 6: Techniques for increasing the Signal-Noise ratio in the processing of Deep Space Images
Introduction:
Capturing deep space objects through telescopes and dedicated astrophotography cameras has faced challenges due to inherent restrictions. Objects emit in various wavelengths, requiring extensive light accumulation. This project addresses these limitations, proposing innovative methods to improve the signal-to-noise ratio.
Methodology:
The project introduces three key methods:
Inclusion of Satellite-Traced Photos: Photos with satellite traces are not discarded if they don’t interfere with the object of interest. Stars are separated, and digital correction of trails preserves valuable information.
Luminance Channel Switch: In nebulas with high hydrogen alpha concentration, this channel replaces conventional luminance. This technique provides a broader detail base, enhancing the final image quality.
Variant of Method 2 – Hydrogen Alpha Channel Use: The hydrogen alpha channel is used instead of the red channel or both combined, avoiding luminance. This combination offers greater detail and a wider contrast range in specific celestial objects.
Results:
The proposed methods underwent intensive testing over a two-week period, capturing diverse deep space objects. Results were highly successful, demonstrating a significant signal-to-noise ratio improvement and enhanced astronomical detail representation.
Targets captured and processed using the methods explained above:
Andromeda
Veil Nebula
Orion Nebula
Pleiades
Pacman Nebula
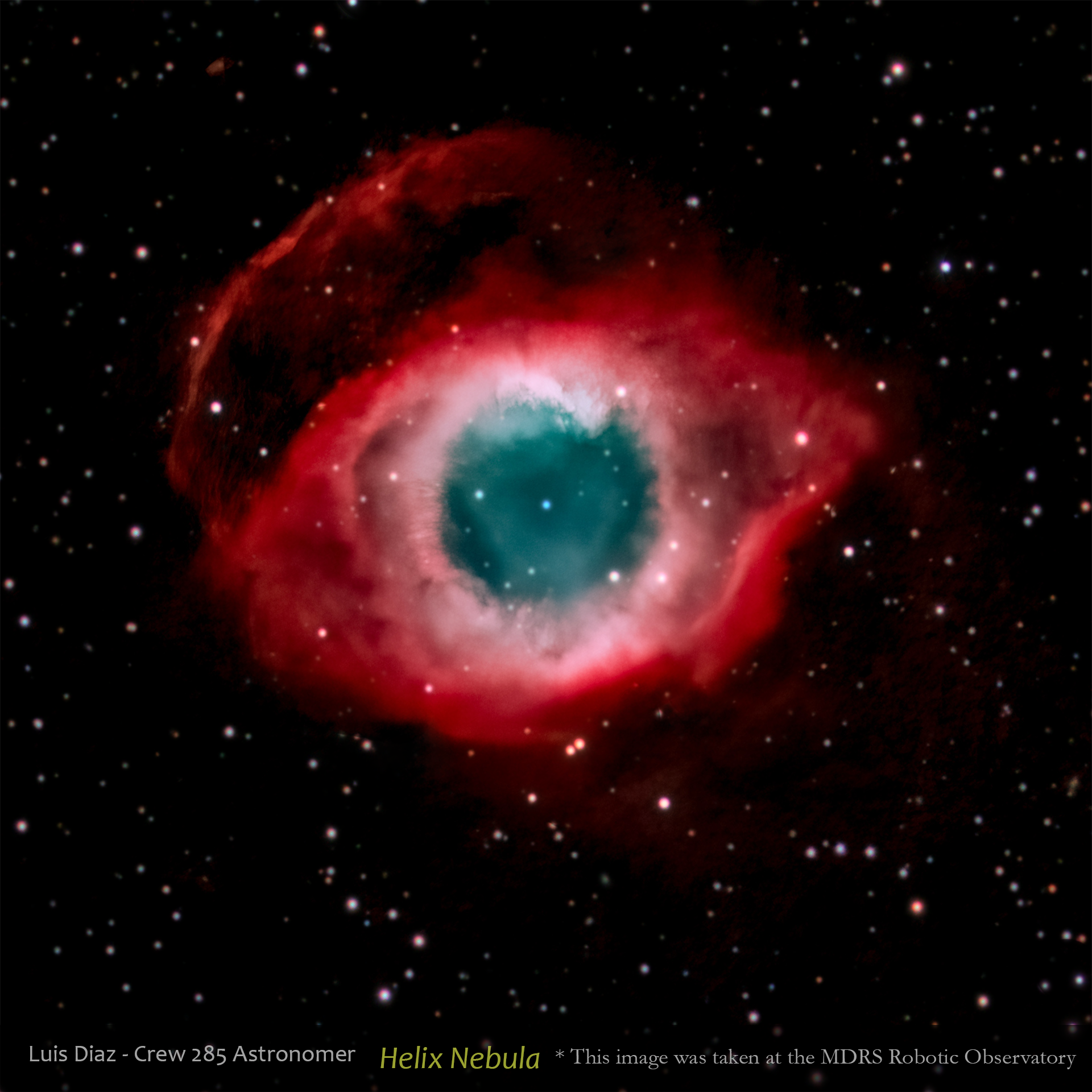
Helix Nebula
Horsehead and Flame Nebulas
Rosette Nebula
Triangulum Galaxy
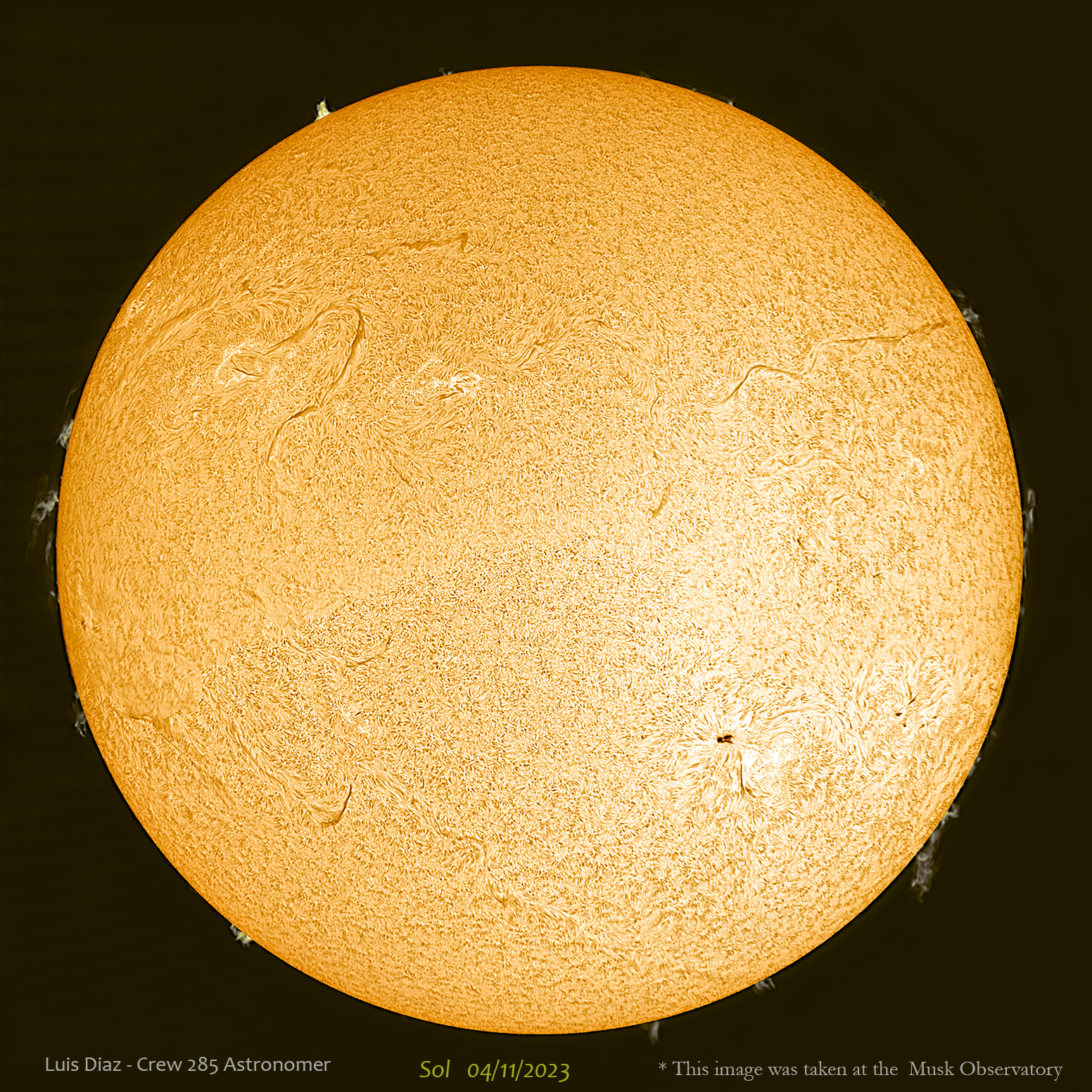
* Extra pictures: Sun, taken with the Musk Solar Observatory

Conclusions:
This project identifies effective strategies to overcome traditional limitations in deep space object capture. The inclusion of satellite-traced images, selective channel switching, and luminance method variants prove promising. Findings open new perspectives for the astrophotography community, providing practical and efficient solutions to enhance image quality in challenging light conditions or situations in which very little light time was accumulated.
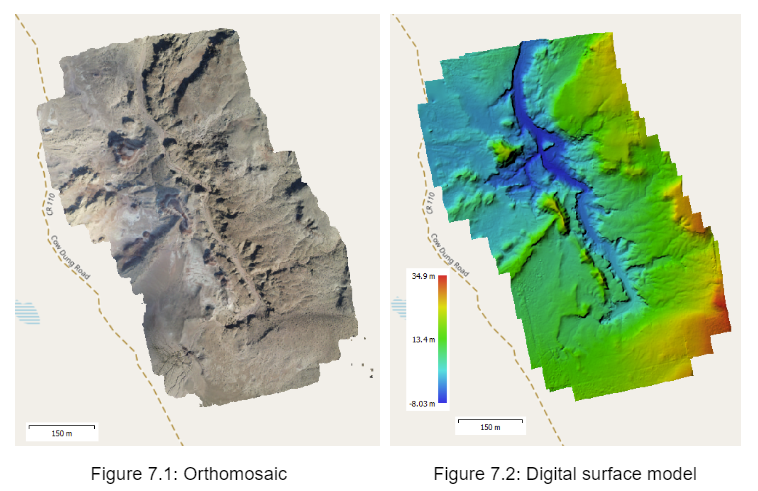
Project 7: Generation of 3D maps and orthomosaics of explored canyons to obtain geographic information and identification of access routes in EVA’s using Drones
Introduction:
Extravehicular Activities (EVAs) are integral to analog simulation missions like those at the Mars Desert Research Station (MDRS). However, navigating canyons during EVAs poses challenges due to unclear access routes. To address this, we proposed leveraging advanced technologies, including drones and 3D modeling, to map and optimize these routes.
Methodology:
The project utilized drones to capture images for creating 3D models, orthomosaics, and digital elevation models. Areas of interest were programmed from a habitat-based web platform, establishing a route plan for automated drone flights. Post-capture, images underwent processing for stitching and point cloud generation, forming the basis for 2D and 3D graphics. The resultant graphics were then used for succeeding EVAs performed by the team, carrying with them digital maps previously generated and carefully planned.
Results and Conclusions:
The project successfully mapped three canyons, Candor Chasma, El Dorado, and Tharsis Montes, providing detailed views and essential data for estimating distances and travel times. This approach enhances safety by identifying optimal access routes. The automated flight plan execution from the web platform proved efficient and easily applicable. The integration of geospatial analysis tools facilitated planning and demonstrated the potential of these technologies in analog environments, supporting efficiency and safety in rugged terrain exploration during EVAs.






















You must be logged in to post a comment.